A hub definition is a central point or device that connects multiple devices, networks, or systems, facilitating the exchange of data and resources. Hubs play a vital role in various contexts, from networking to transportation, enabling efficient and seamless communication.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of hubs, exploring their types, components, benefits, challenges, and future trends. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business professional, or simply curious about the inner workings of connectivity, this article will provide you with a thorough understanding of hubs and their impact on modern technology.
Definition of a Hub
A hub, in its most fundamental sense, serves as a central connection point that facilitates the exchange of information, resources, or services. It acts as a conduit through which multiple entities can interact and communicate with each other, enabling seamless data flow and collaboration.
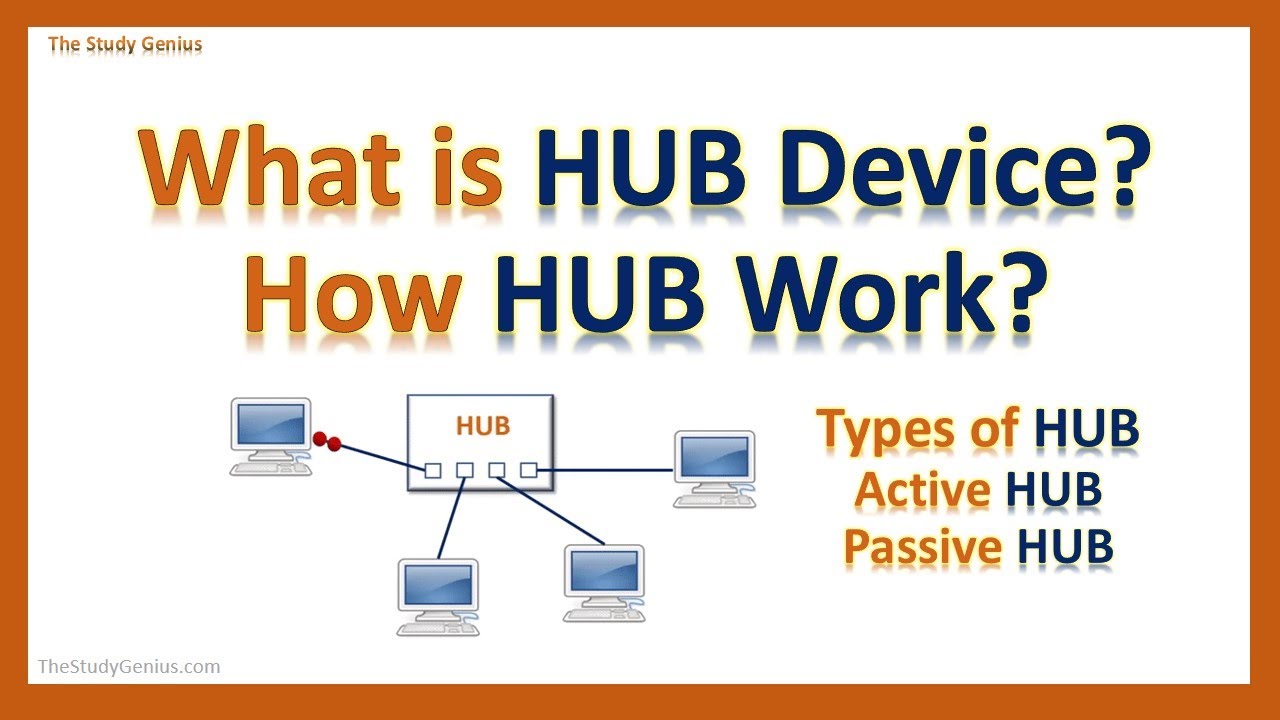
Hubs can manifest in various forms, depending on the context in which they are employed. In the realm of networking, a hub is a physical device that connects multiple computers or devices within a local area network (LAN), allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other.
In the context of transportation, a hub refers to a central transportation facility that serves as a convergence point for different modes of transportation, such as airports, train stations, or seaports.
The primary purpose of a hub is to provide a centralized platform for connectivity and data exchange. It serves as a focal point that facilitates the efficient and secure transfer of information, resources, and services among interconnected entities.
Types of Hubs
Hubs can be broadly categorized into various types based on their specific functions and applications. Some of the most common types of hubs include:
- Network Hub:A physical device that connects multiple computers or devices within a local area network (LAN), allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other.
- Transportation Hub:A central transportation facility that serves as a convergence point for different modes of transportation, such as airports, train stations, or seaports.
- Logistics Hub:A facility that serves as a central point for the storage, distribution, and transportation of goods and materials.
- Data Hub:A centralized repository for data collection, storage, and dissemination. It provides a single point of access to data from multiple sources, enabling data analysis and insights.
- Innovation Hub:A collaborative workspace that brings together individuals, organizations, and resources to foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
Components of a Hub
The components of a hub vary depending on its type and purpose. However, some common components include:
| Component | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Network Interface Card (NIC): | Connects the hub to a computer or device. | Ethernet cards, Wi-Fi adapters |
| Ports: | Physical or virtual connections that allow devices to connect to the hub. | Ethernet ports, USB ports |
| Central Processing Unit (CPU): | Manages the hub’s operations and data flow. | Microprocessors, embedded systems |
| Memory: | Stores data and instructions for the hub’s operation. | RAM, ROM |
| Software: | Controls the hub’s functionality and manages data flow. | Operating systems, firmware |
Benefits and Applications of Hubs
Hubs offer numerous benefits and have wide-ranging applications across various industries. Some of the key benefits include:
- Centralized Connectivity:Hubs provide a single point of connection for multiple entities, simplifying network management and data exchange.
- Improved Efficiency:By centralizing data and resources, hubs streamline operations and reduce the time and effort required for data retrieval and sharing.
- Enhanced Collaboration:Hubs foster collaboration by providing a platform for interconnected entities to share information, ideas, and resources.
- Increased Productivity:Hubs enable faster and more efficient data transfer, leading to increased productivity and improved decision-making.
Hubs find applications in a diverse range of industries, including:
- Networking:Connecting devices within a LAN or WAN, enabling data sharing and communication.
- Transportation:Facilitating the seamless transfer of passengers and goods between different modes of transportation.
- Logistics:Optimizing the storage, distribution, and transportation of goods.
- Data Management:Providing centralized access to data from multiple sources, supporting data analysis and insights.
- Innovation:Creating collaborative environments that foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
Challenges and Limitations of Hubs

While hubs offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain challenges and limitations:
- Single Point of Failure:If the hub fails, it can disrupt connectivity and data flow for all connected entities.
- Security Vulnerabilities:Hubs can be vulnerable to security breaches, as they provide a single point of entry for unauthorized access.
- Scalability:Hubs may have limited capacity and may not be able to accommodate a large number of connected devices or handle high volumes of data.
- Cost:Implementing and maintaining hubs can be expensive, especially for large-scale networks or complex systems.
To overcome these challenges, organizations can implement redundant systems, enhance security measures, and carefully plan for scalability. Additionally, choosing the right type of hub for the specific application is crucial to mitigate potential limitations.
Future Trends and Innovations in Hubs
The future of hubs is promising, with emerging trends and innovations shaping their evolution:
- Virtualization:Virtual hubs are gaining popularity, providing greater flexibility and scalability in network and data management.
- Cloud-Based Hubs:Cloud computing is enabling the development of cloud-based hubs that offer centralized access to data and resources from anywhere.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI is being integrated into hubs to automate tasks, optimize data flow, and enhance security.
- Internet of Things (IoT):Hubs are playing a crucial role in connecting IoT devices and facilitating data exchange within smart cities and industries.
As technology continues to advance, hubs will continue to evolve, offering innovative solutions for connectivity, data management, and collaboration in various fields.
Summary: Hub Definition
In conclusion, hubs have become indispensable components of our interconnected world, facilitating communication, collaboration, and innovation across industries. As technology continues to advance, hubs will undoubtedly evolve, offering even more powerful and versatile solutions for connecting and managing devices, networks, and systems.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of a hub?
A hub’s primary function is to connect multiple devices, networks, or systems, allowing them to communicate and exchange data.
What are the different types of hubs?
Hubs can be categorized into various types, including network hubs, USB hubs, power hubs, and transportation hubs.
What are the advantages of using hubs?
Hubs offer several advantages, such as centralized connectivity, increased bandwidth, improved efficiency, and simplified network management.